Abstract
Background Outcomes of patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) have historically been poor, particularly for those who are ineligible for or progress after autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). The L-MIND study evaluated tafasitamab/lenalidomide (TL) in selected patients with R/R DLBCL who were ineligible for ASCT, with encouraging findings including overall response rate (ORR) of 60%, complete response rate (CRR) of 43%, median progression-free survival (PFS) of 12.1 months, and median overall survival (OS) of 33.5 months (Salles et al., Lancet Onc 2020; Duell J. et al., Haematologica 2021). We performed a multicenter retrospective study to determine real-world characteristics of TL recipients, patterns of TL administration, and outcomes of treatment since US FDA approval.
Methods We performed a retrospective study of all patients with R/R DLBCL treated with TL outside of a clinical trial at 9 institutions. Data on demographics, medical comorbidities, diagnosis, prior therapies and responses to prior therapies, adverse events (AEs) after TL, and ORR, CRR, PFS, and OS after initiation of TL were extracted from electronic medical records. Subgroup analyses evaluating outcomes in patients with prior chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) or other anti-CD19 therapy, primary refractory disease to initial therapy, relapsed vs refractory disease to last treatment, number of prior therapies, and IPI were also performed. ORR and CRR were compared using Fisher's exact test. PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and differences in curves were tested by the log-rank test.
Results A total of 82 patients from 9 institutions were evaluated; all received at least 1 dose of tafasitamab and lenalidomide for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Overall, 75 (91%) of patients did not meet L-MIND study eligibility criteria; reasons for ineligibility included more than 3 prior lines of therapy (28%), prior anti-CD19 therapy (23%, including 21% with prior CAR T), HGBCL (13%), ECOG performance status 3-4 (18%), and renal dysfunction (EGFR < 60 ml/min) (33%). Dose delays in lenalidomide initiation occurred in 45% of patients; in patients with delays, median time between first tafasitamab and first lenalidomide was 7 days (range 1-78). Lenalidomide dose reductions at initiation occurred in 54% of patients, most commonly due to renal dysfunction (35%), performance status/frailty (18%), or cytopenias (9%).
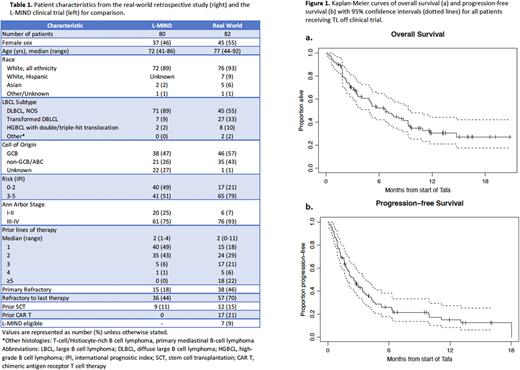
ORR for the entire cohort was 27% (95% CI 19-39), with CRR 17% (95% CI 10-27). Median PFS was 2.8 months (95% CI 1.8 - 3.6), and median OS 6.8 months (95% CI 4.9 - 9.3). Compared to refractory disease, relapsed disease to last therapy (defined as best response of PR or CR to last treatment, and relapse at least 6 months after treatment) was associated with better CRR (40% vs 7%, OR 8.5, p < 0.01), PFS (median 4.7 vs 1.9 mo, HR = 0.44; p < 0.01), and OS (median 9.6 vs 5.1 months, HR = 0.48; p = 0.03). Lower IPI score (0-3 vs 4-5) was associated with longer PFS (3.6 vs 1.7 mo, HR = 0.51 , p < 0.01) and OS (median 9.3 vs 3.4 mo, HR = 0.46, p < 0.01). Fewer prior lines of therapies (0-2 vs ≥3) was associated with longer PFS (3.6 vs 1.8 mo, HR 0.58; p = 0.03) but was not significantly associated with OS (9.3 vs 5.7 months, HR 0.74; p = 0.29).
Prior CAR T or other CD19 therapy were not associated with worse CRR, PFS or OS. Median time from CAR T therapy to TL initiation was 14.3 months. Of 6 patients with refractory disease to CAR T, 1 of 6 achieved CR to TL (ORR 17%, CRR 17%), while 4 of 11 patients with relapsed disease after CAR T achieved CR (ORR 36%, CRR 36%).
Conclusions In this real-world study of TL in R/R LBCL, clinical outcomes including ORR, CRR, PFS and OS were lower than observed in the L-MIND phase 2 clinical trial. These differences may be related to a greater incidence of high-risk disease features among real-world patients, higher rates of comorbidities, and frequent delays and dose reductions in lenalidomide treatment. Patients with relapsed disease to last therapy, low-moderate IPI (0-3), and fewer prior lines of therapy (0-2) had better outcomes than patients without these features, identifying a population that may derive the most benefit from TL treatment. Patients with relapsed disease after CD19-directed CAR T therapy also demonstrated potential for complete responses with TL, suggesting this regimen is a feasible approach in the post-CAR T setting.
Disclosures
Caimi:Genmab: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rutherford:Genentech: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Dova: Consultancy; Celgene/Juno: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy. Romancik:AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Leslie:Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Celegene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Jansssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Speakers Bureau; Eli Lily: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kahl:Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; AcertaPharma: Consultancy; MEI: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy; ADT Therapeutics: Consultancy; Hutchmed: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Research To Practice: Speakers Bureau. Maddocks:Incyte: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy; Lilly: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Salles:Roche/Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Celgene, Novartis, MorphoSys AG, Epizyme, Alimera Sciences, Genmab, Debiopharm Group, Velosbio, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BeiGene, Incyte, Miltenyi Biotec, Ipsen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Loxo, Rapt: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech, Janssen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, AbbVie, MorphoSys AG, Amgen, Bayer, Epizyme, Regeneron, Kite, a Gilead Company: Honoraria; AbbVie, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Debiopharm, Epizyme, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Incyte, Kite, a Gilead Company, Miltenyi, MorphoSys, Takeda, and VelosBio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Batlevi:Dava Oncology: Other: Provision of Services; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Life Sciences: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Juno/Celgene: Consultancy; GLG Pharma: Consultancy; Xynomic: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Ownership / Equity Interests; Provision of Services; Janssen: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Other: Provision of Services; Autolus: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Epizyme: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal